WHAT IS POCSO
A quick glance at our new law for protecting children from sexual offences.
POCSO is the acronym for ‘Protection of Children against Sexual Offences Act’ of 2012. With its enactment, India now has one of the most comprehensive and ambitious laws that not only allows justice for children who are victims of sexual offences but also takes into account the best interests and well-being of the child. It is a landmark legislation in the area of child protection.

Before POCSO
Before the new law was passed, there were no specific laws which addressed sexual crimes against children. Most cases would be considered under sections in the Indian Penal Code that dealt with rape, unnatural offences or sections even more ambiguous and imprecise such as ‘outraging the modesty of a woman’. Offences like child pornography, harassment and stalking proved difficult to prosecute.
GENDER NEUTRAL
What Makes POCSO comprehensive?
- POCSO puts the burden of proof on the accused rather than the victim. The onus is on the accused to prove that he/she is innocent rather than on the child to prove that the crime took place.
- POCSO is gender neutral when it addresses the victims and the accused.
- POSCO addresses a comprehensive spectrum of criminal sexual offences that includes various forms of (partial) penetrative offences, non-touch forms of abuse, pornography, exhibitionism, stalking etc.
- POCSO takes into account power dynamics in relationships between the victim and the accused. The vulnerability of the victim and the position of accused play a major part in the prosecution of the crime.
- POCSO provides for child-friendly measures, procedures and infrastructure to ensure minimum trauma is visited upon the child during the judicial process.
- POCSO regards Child Protection as a collective responsibility. It makes the reporting of cases mandatory for every citizen. It also lays out guidelines for all duty-bearers and stakeholders who interact with the child victim and the case.
Click below to download the ‘Whats POCSO’ infographic
Some Definitions Under POCSO
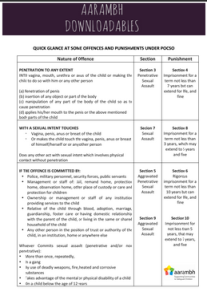
Child: Any person below the age of 18 years
Penetrative sexual assault: Penetration to any extent INTO vagina, mouth, urethra or anus of the child or making the child to do so with him/her or any other person
- penetration of penis
- insertion of any object or part of the body
- manipulation of any part of the body of the child so as to cause penetration
- applying his/her mouth to the penis or the above mentioned body parts of the child
Sexual assault: When a person, with sexual intent, touches the
- Vagina, penis, anus or breast of the child
- Or makes the child touch the vagina, penis, anus or breast of himself/herself or any other person
- Or does any other act with sexual intent which involves physical contact without penetration.
Aggravated Sexual Assault: If the offence is committed by a person in a position of trust or authority like teachers, police, parents, public servants etc or if the child is below 12 yrs or if the child is disabled or if the injury to the child is grievous or if the child becomes pregnant, the assault is termed as ‘aggravated’.
Click below to download the ‘Aggravated Offences’ Infographics
Sexual harassment: If a person, with sexual intent, is
- Making any sound or gesture or exhibiting any object or part of the body so that it shall be heard by the child or such gesture or exhibition shall be seen by child.
- Making a child exhibit any part of his/her body so that it is seen by the person or any other person.
- Constantly following or watching the child either directly or through digital or any other means
- Showing any object to the child in any form or enticing the child for pornographic purposes
Abetment: If the accused is found instigating, conspiring and intentionally aiding any of the above acts, in any manner, it is an abetment offence. The punishment is same as that provided for the offence.
Mandatory Reporting: Any person who has apprehensions that any of the above offences is likely to be committed or has been committed must report it to the local police or Special Juvenile Police Unit(SJPU).
COMMITTED TO PROTECT
CHILD FRIENDLY
Procedures Under POCSO
Child-friendly Judicial Processes
POCSO provides for child-friendly procedures for medical examination, recording the statement of the child by the police and Magistrate, as well as during the examination of the child in court.
- POCSO mandates the establishment of child-friendly Special Courts at every district.
- During the above procedures, a child must be accompanied by a parent, guardian, or any other person whom the child trusts or has confidence in.
- The child must not be brought face to face with the accused while giving her/his statement to the Police or the Magistrate, or while testifying.
Emergency Medical Care
Children who are victims of penetrative sexual assault, aggravated penetrative sexual assault, sexual assault, and aggravated sexual assault; or who are found to be in need of urgent medical attention are entitled to receive emergency medical care within 24 hours of the Police/Special Juvenile Police Unit (SJPU) receiving information about the crime.
Care and Protection
- If the Police/SJPU have reasonable grounds to believe that the child is in need of care and protection, they must immediately make arrangements to give the child such care and protection.
- They must alert the Child Welfare Committee (CWC). The CWC can assess the case and take steps to ensure that the child is provided with suitable care and protection.
- For instance, it can provide the child with a support person to render assistance during the investigation and trial.
- It can also order that the child be taken out of the custody of her/his family if she/he has been or is likely to be sexually abused there.
Compensation
A child victim may receive interim compensation for immediate need for relief or rehabilitation and final compensation for the loss or injury caused to him or her. Compensation is given irrespective of whether the accused is found guilty or not.
Download The Complete Text of POCSO
Click here to download and read the complete text of the Protection of Children From Sexual Offences (POCSO) Act, 2012.
Guidelines Under POCSO
Click here to download Guidelines for National and State Commission for Protection of Child Rights (NCPCR/SCPCR) for Roles and Functions of Various Stakeholders
Challenges with POCSO
Some of the widely discussed and debated challenges in implementing POCSO are mandatory reporting of sexual offences and age of consent for sexual activity between two minors. Infrastructure and implementation of child friendly procedures is yet another concern. One also needs to look at the monitoring of how the law is being implemented across various states.
Here are some links to articles written on the challenges under POCSO:
Love & Sex in times of POCSO, Swagata Raha
Mandatory Reporting of Child Sexual Abuse in India? Are we ready for it?, Uma Subramanian
Strong provisions weak implementation, Anil Malhotra
CHALLENGES CONTINUE